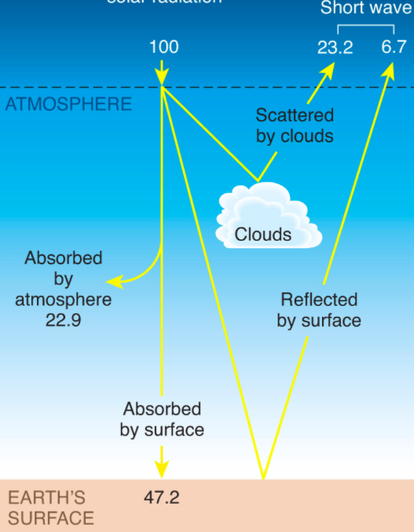
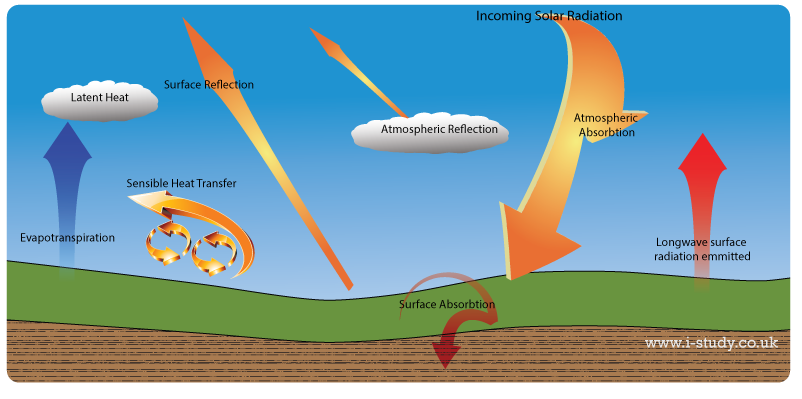
Heat emitted from Earth's surface is absorbed by gases in the atmosphere and then reradiated back to the surface Here 100 energy units = 556e24J/year, the total annual solar energy received averages 342 W/m^@ over theGreenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases areQuantitative analysis Energy flows between space, the atmosphere, and Earth's surface, with greenhouse gases in the atmosphere capturing a substantial portion of the heat reflected from the earth's surface The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this
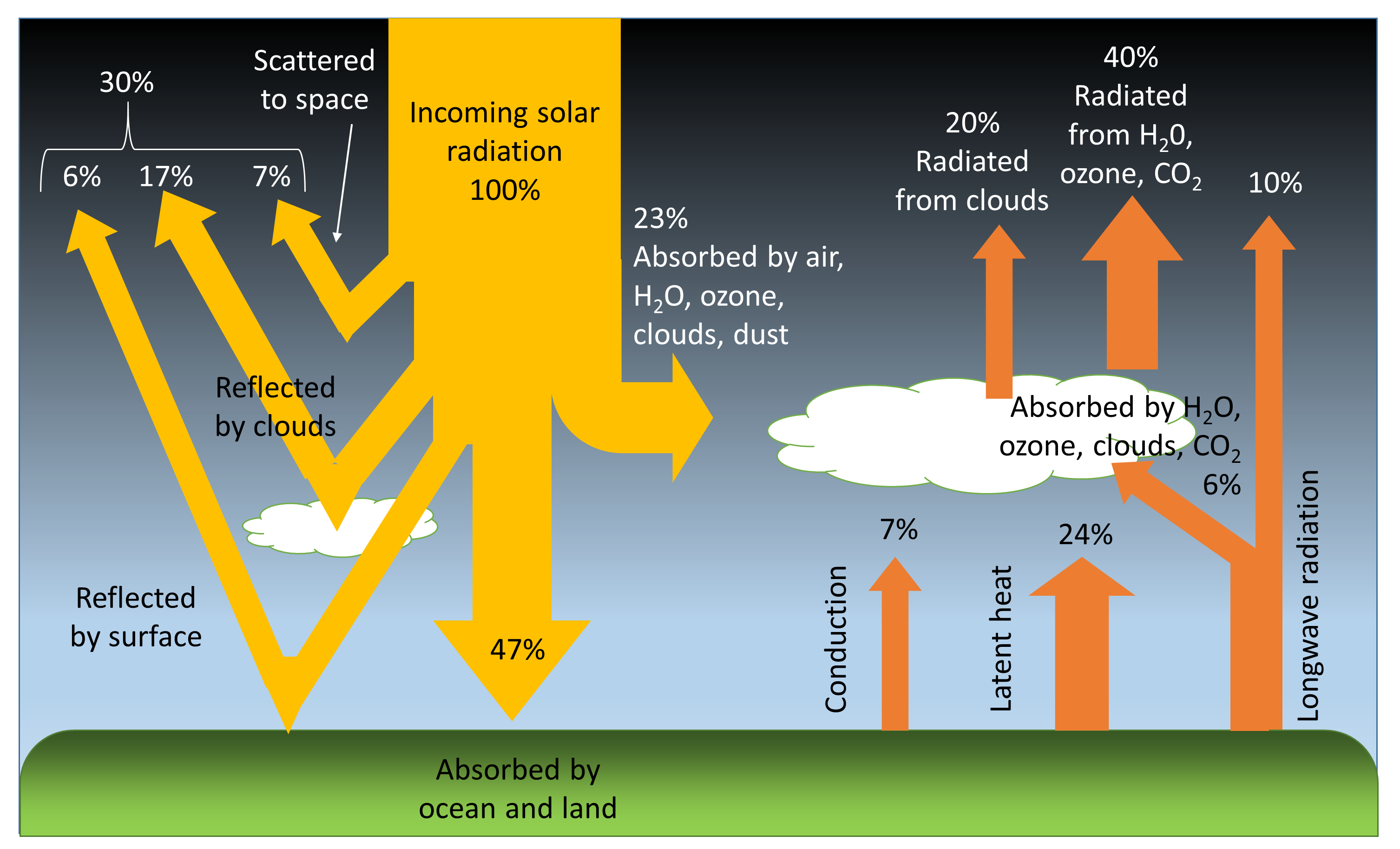
8 1 Earth S Heat Budget Introduction To Oceanography
Greenhouse effect definition world geography
Greenhouse effect definition world geography- The "greenhouse effect" is the warming that happens when certain gases in Earth's atmosphere trap heat These gases let in light but keep heat from escaping, likeGreenhouse effect definition The greenhouse effect is the problem caused by increased quantities of gases such as Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Course Help
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinated gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Greenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heatGreenhouse gas noun any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effectOverview Earth is now in an icehouse state, and ice sheets are present in both poles simultaneously Climatic proxies indicate that greenhouse gas concentrations tend to lower during an icehouse Earth Similarly, global temperatures are also lower under Icehouse conditions
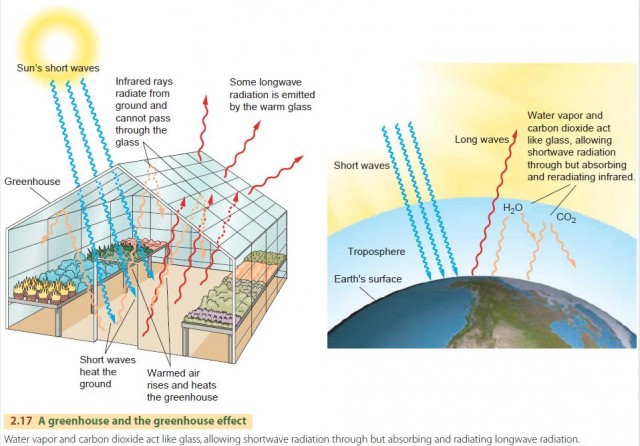
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without themGreenhouse effect grēn ′hous′ The retention of part of the Sun's energy in the Earth's atmosphere in the form of heat as a result of the presence of greenhouse gases Solar energy, mostly in the form of shortwavelength visible radiation, penetrates the atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surfaceThe "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect works
Known as the Greenhouse Effect, this process is essential to life as we know it Without it, Earth's surface temperature would be significantly lower andThe greenhouse effect is a naturallyoccurring phenomenon on the earth as it is on Venus The enhancement of this effect by increasing greenhouse gases associated with manmade activities is the reason for concern about climate change This process is known as the greenhouse effect because it is similar to how a greenhouse works the sun's energy passes through the glass (or similar) panes of the greenhouse, but not all of it is allowed to escape again, making the inside of the greenhouse a warmer and more hospitable environment for the plants inside




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet
Greenhouse effect n A phenomenon in which the atmosphere of a planet traps radiation emitted by its sun, caused by gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane that allow incoming sunlight to pass through but retain heat radiated back from the planet's surfaceThe greenhouse effect occurs when certain in the Earth's atmosphere (the air around the Earth) trap infrared radiationThis makes the planet become warmer, similar to the way it makes a greenhouse become warmer The greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases;Global warming definition, an increase in the earth's average atmospheric temperature that causes corresponding changes in climate and that may result from the greenhouse effect See more



Geography And Environment




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Global Warming Project Greenhouse Effect Global Warming
Increased greenhouse gases and the greenhouse effect has contributed to an overall warming of the Earth's climate, leading to a global warming (even though some regions may experience cooling, or wetter weather, while the temperature of the planet on average would rise)Greenhouse effect Y The trapping of heat radiation around the Earth by excess greenhouse gases produced through human activity Explosivity Y A measure of the relative explosiveness of volcanic eruptions varying due to formation on convergent or divergent boundaries Greenhouse gases Human activities such as energy, industry,Writing About Geography 8 Expository Writing Review the text in Section 1 about global warming Then write a paragraph explaining the ways in which agriculture may be affected heat escapes, the plants will freeze If too much heat is trapped, the plants will wilt or dry out The greenhouse effect of Earth's atmosphere fol
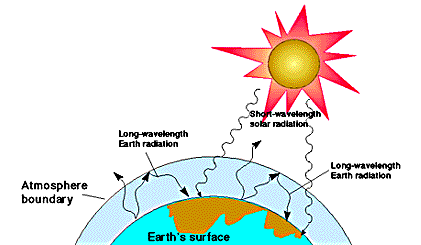



Greenhouse Effect Its Causes And Effect List Of Greenhouse Gases




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Definition Impact Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
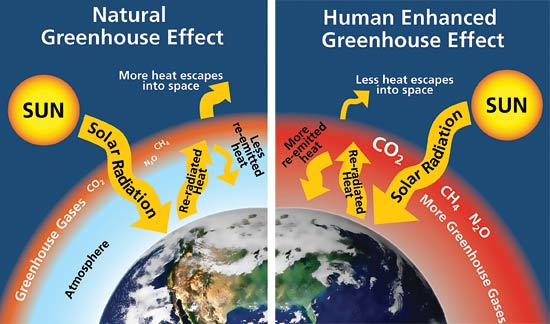
Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases actFigure 31 The matrix of geographic perspectives Geography's ways of looking at the world—through its focus on place and scale (horizontal axis)—cuts across its three domains of synthesis humansocietal dynamics, environmental dynamics, and environmentalsocietal dynamics (vertical axis)The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, but the extra gases produced by human activity are making it stronger We are now adding to these gases faster than oceans and plants can absorb them — the greenhouse effect is being 'enhanced' by humans There is strong evidence that recent changes are unprecedented and not due to natural




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
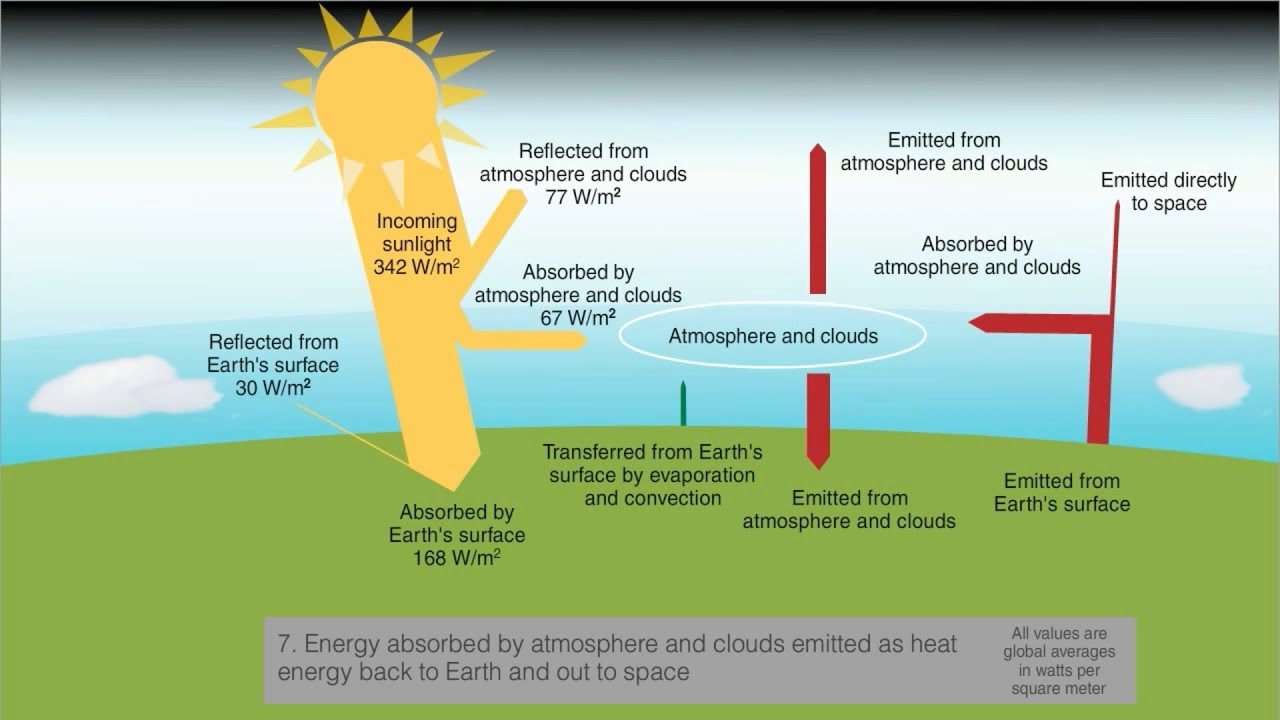



Atmosphere Change 4hrs Geography For 21 Beyond
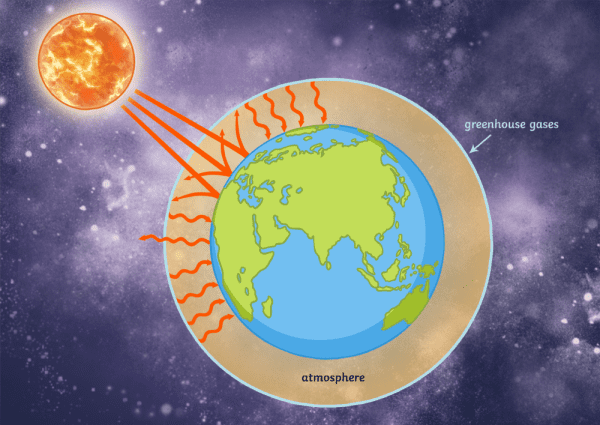
Natural processes removed as much carbon from the atmosphere as they released Human activities like burning fossil fuels have added huge quantities of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide to our atmosphere, creating a "greenhouse effect" that traps energy from the sun and causes Earth's temperature to rise See all related content → greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gasesWhen energy from the sun enters Earth's atmosphere, greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere such as carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor absorb some of the energy and radiate some of it either back into space, to other molecules in the atmosphere, or to Earth's surface This effect helps maintain Earth's temperature




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Course Help




How The Greenhouse Effect Works Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Greenhouse Gases
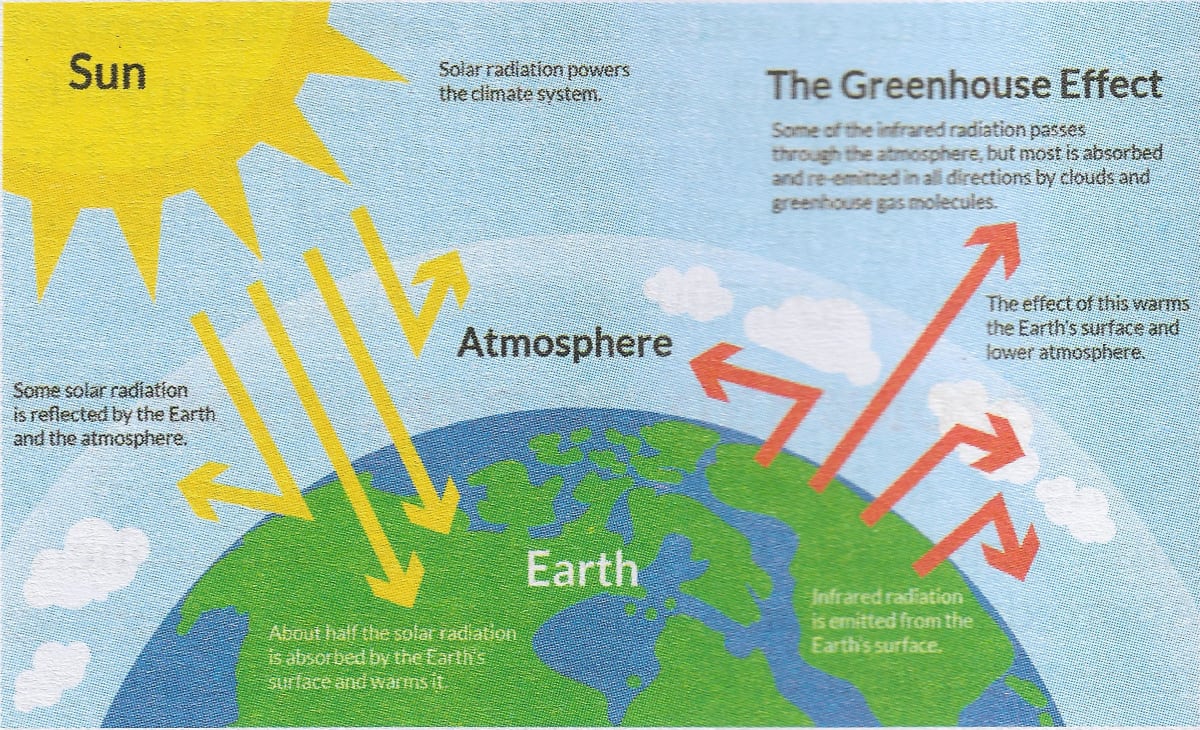
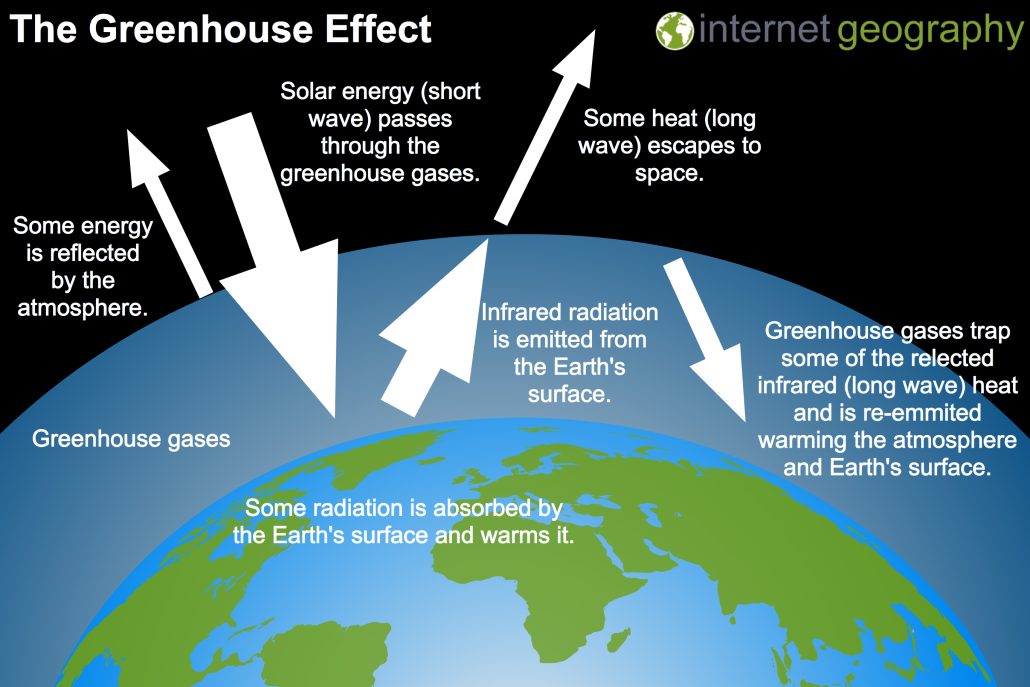
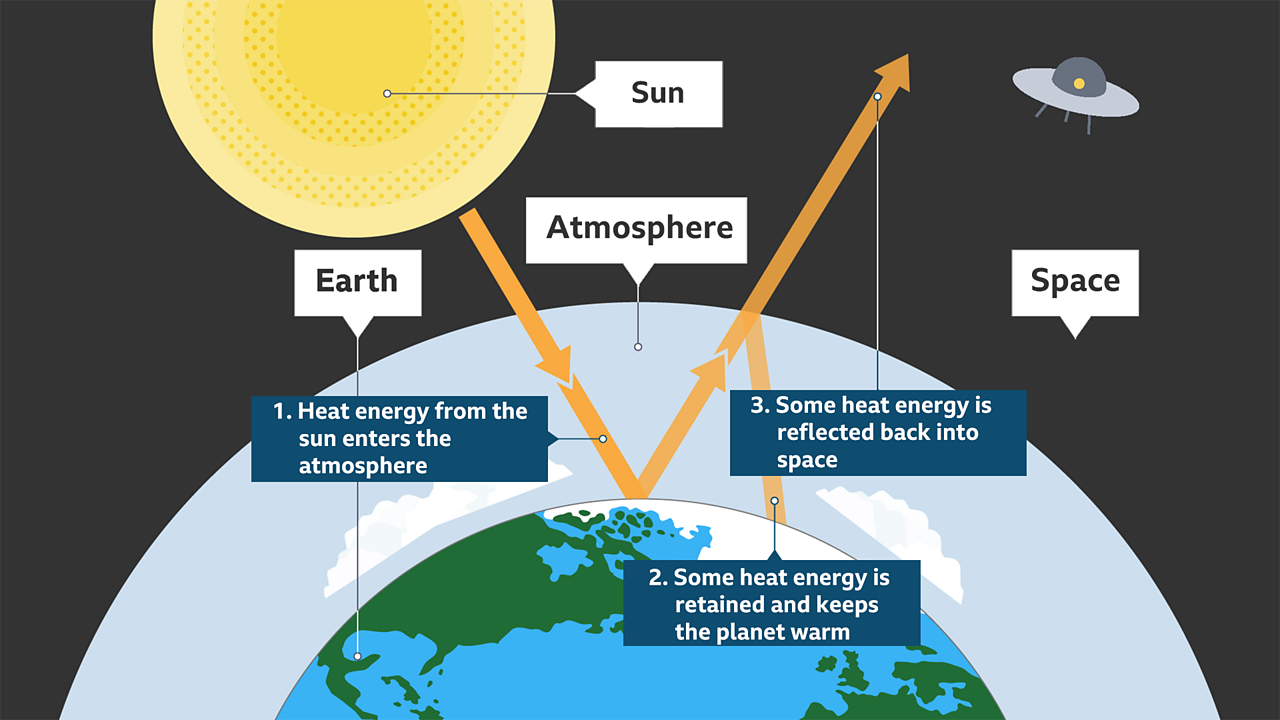
A greenhouse stays warmer than the air outside Instead of cooling off at night, it traps some of the heat inside to keep the plants warmGreenhouse effect Step 1 Solar radiation reaches the Earth's atmosphere some of this is reflected back into space Step 2 The rest of the sun's energy is absorbed by the land and the oceans, heating the Earth Step 3 Heat radiates from Earth towards space Step 4 Some of this radiative heat is trapped by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, keeping the Earth warm Definition of greenhouse effect warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to
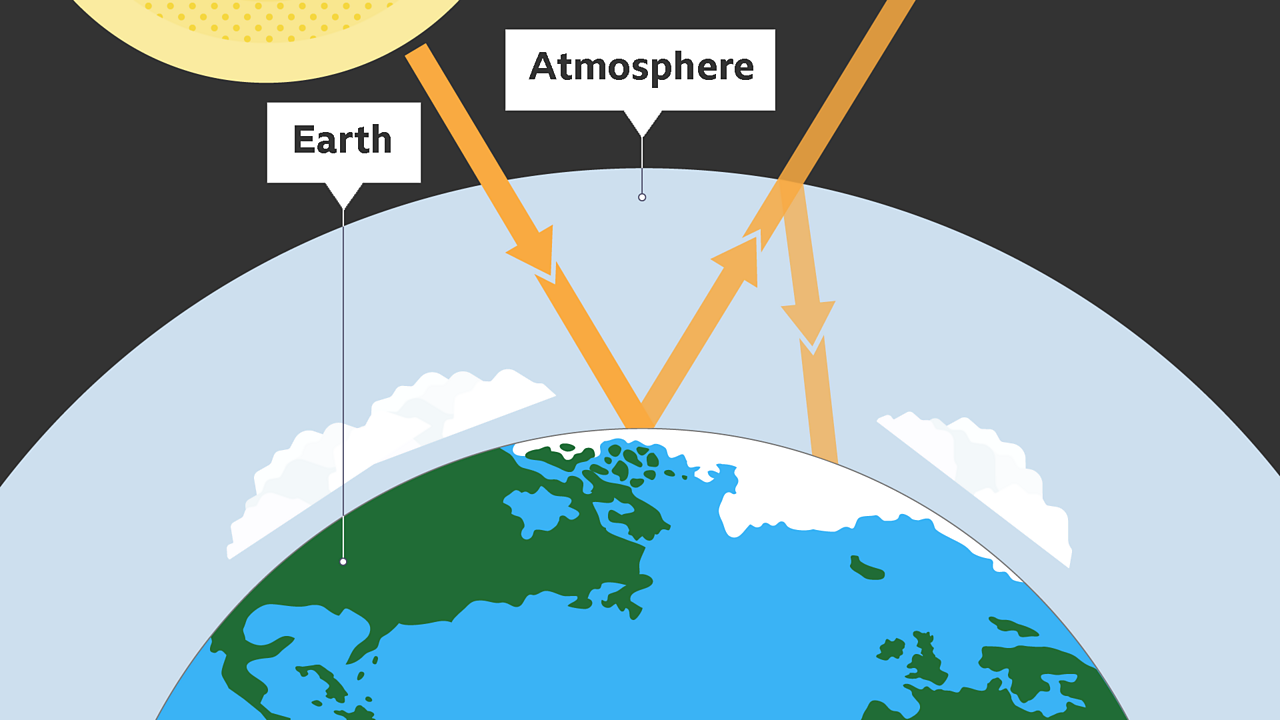



Climate Change Ks3 Geography c Bitesize c Bitesize



Chapter 12 Composition And Structure Of The Atmosphere Solutions For Class 9 Icse Total Geography Morning Star Knowledgeboat
The greenhouse effect and global warming 3 Geography Standard 8 Understands the characteristics of ecosystems on Earth's surface Standard 14 To begin the class, ask students to think without talking about a definition for the greenhouse effect Give them a minute to formulate their ideas and then have them write down theirGreenhouse gases remain in the atmosphere for long periods, and act as a 'blanket' around the earth absorbing the infrared radiation from the earth and radiating it back to warm the lower atmosphere – the greenhouse effect Without this effect the earth's temperature would be to 30°C colder and less suitable for life The Greenhouse Effect Life in a greenhouse?




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Conceptual Models Geography Brian Williams
The greenhouse effect traps some of the energy from the Sun, which keeps our planet at a suitable temperature for life The problem is that our increased release of greenhouse gases is causing anAn enhanced greenhouse effect (global warming) the speed of global winds will increase Increased wind speed will cause a greater disturbance of ocean water, which then will cause larger clouds to form The clouds might either increase or decrease the Earth's average global temperature" TASK 1 Yes, by increasing the abundance of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, human activities are amplifying Earth's natural greenhouse effect Virtually all climate scientists agree that this increase in heattrapping gases is the main reason for the 18°F (10°C) rise in global average temperature since the late nineteenth century



What Causes Climate Change Internet Geography




How Cap And Trade Works Environmental Defense Fund
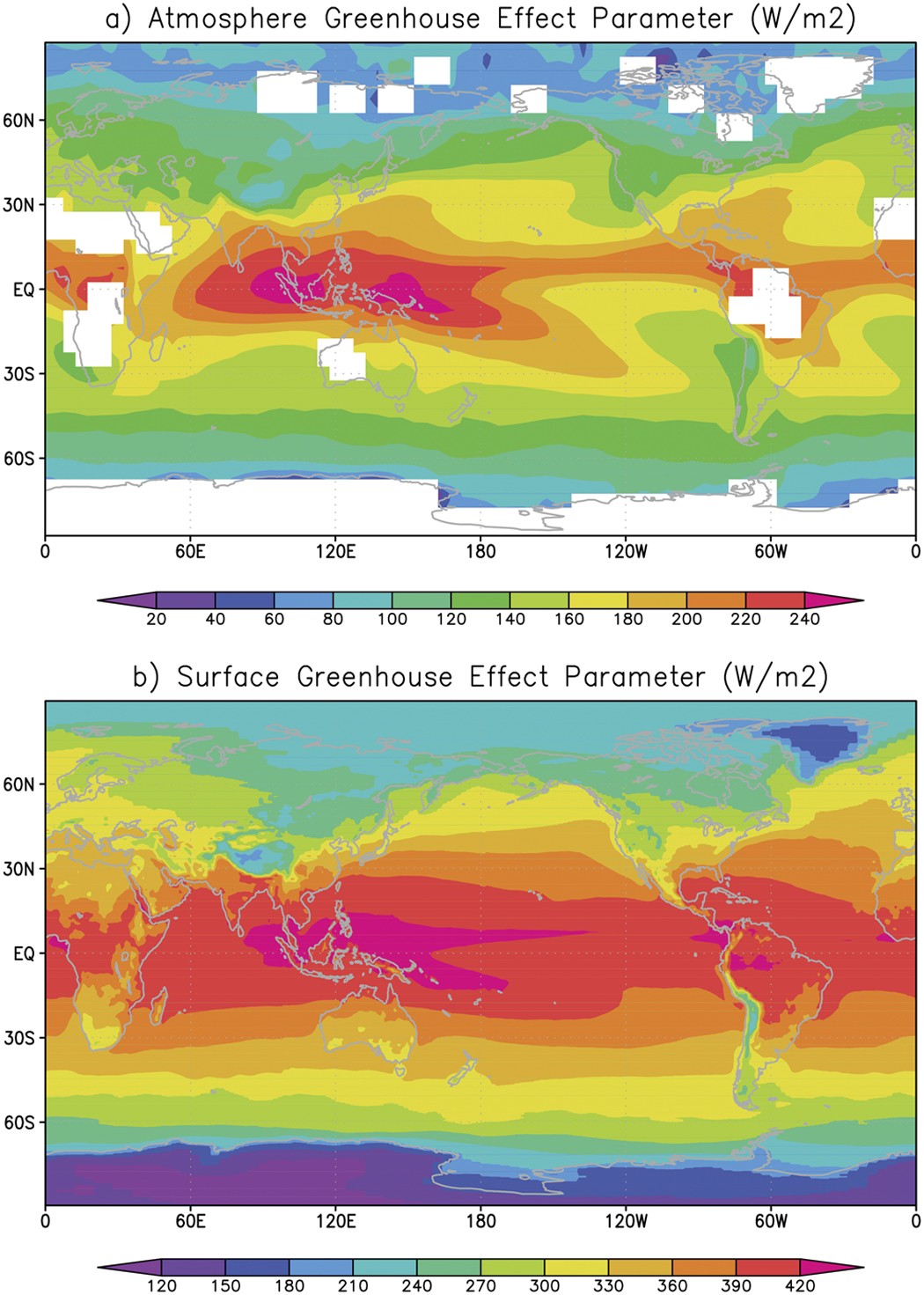
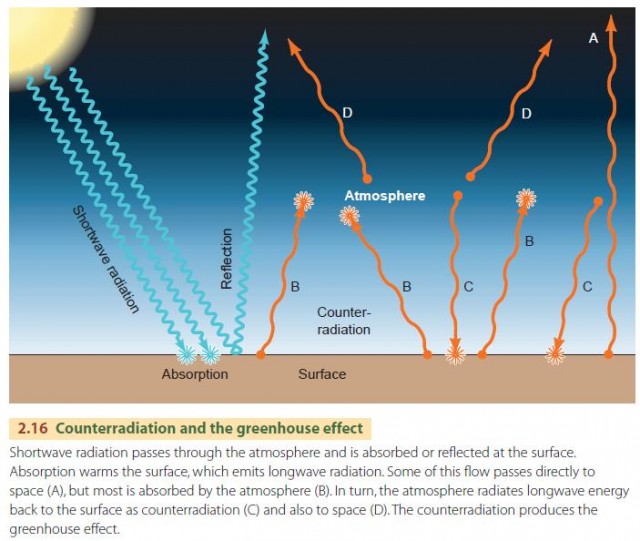
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclearThe most important greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide(CO 2), andThe two large flows on the right represent a kind of energy recycling program that constitutes the greenhouse effect;



Climate Change Ks3 Geography c Bitesize c Bitesize



The Greenhouse Effect
Hence these gases are known as greenhouse gases and the heating effect is known as greenhouse effect Oxides of Nitrogen with general formula NO x – NO, NO 2 – Nitrogen oxide, Nitrogen dioxide etc are global cooling gassesWarming effect of trace gas greenhouse gas is enhanced by the effect of water vapour, which also absorbs infrared radiation, leading to an important natural feedback effect between anthropogenic greenhouse gas and water vapour (Figure 111) A certain level of greenhouse gas is necessary for human life otherwise the planet would be anWhat exactly is the greenhouse effect?Radiation can be described as a flow of elementary particles, photons, each of which has a certain energy, proportional to the frequency of the radiation (see The thermal radiation of the black body)In the atmosphere, when a photon meets a molecule, it can capture its energy, but only under certain conditions



1




The Greenhouse Effect R Electromagnetic Em Radiation Radiation
A greenhouse is for growing plants It is made of glass or clear plastic to let in lots of sunlight But why not just put the plants outside?Define greenhouse gas greenhouse gas synonyms, greenhouse gas pronunciation, greenhouse gas translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse gas n Any of the atmospheric gases that contribute to the greenhouse effectAbsorb heat radiated from the Earth then release energy in all directions, which keeps the Earth warm The diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the




American Heritage Dictionary Entry Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



Greenhouse Gas Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geography Myp Gcse Dp



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki



Geog 7 Lec 1 Images
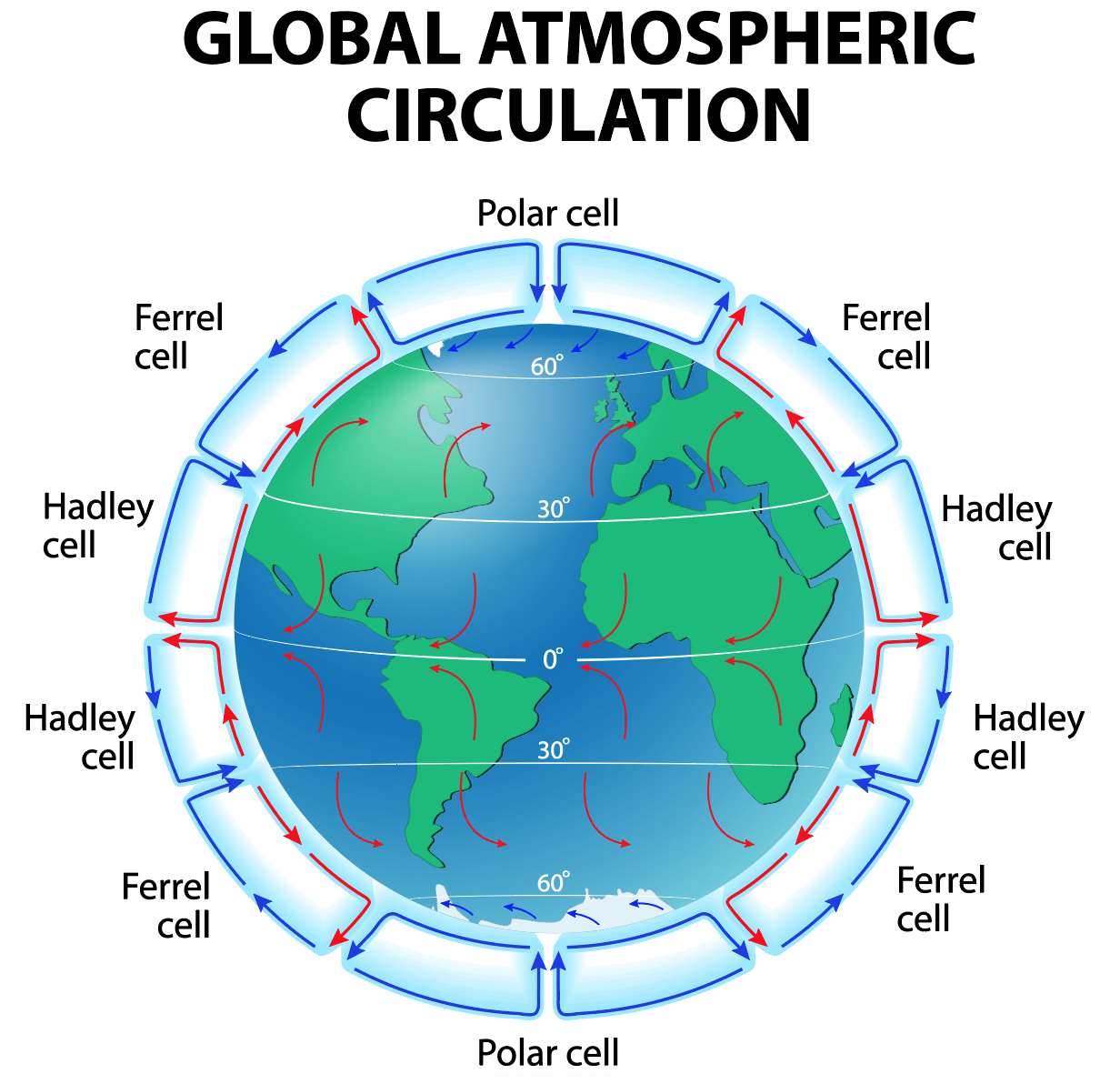



What Is Global Atmospheric Circulation Internet Geography




Article Top 22 Benefits Of Trees Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases
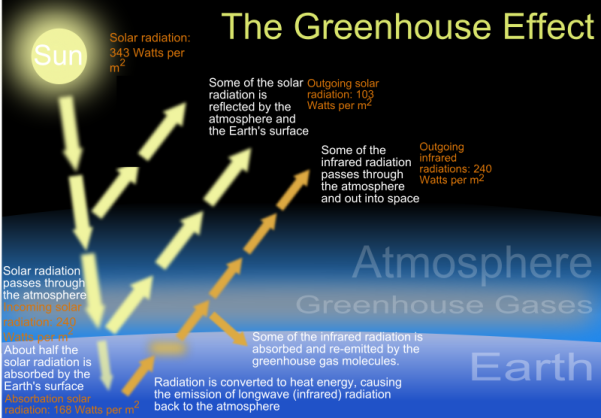



The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com



Pdf Global Warming Effect On Living Organisms Causes And Its Solutions
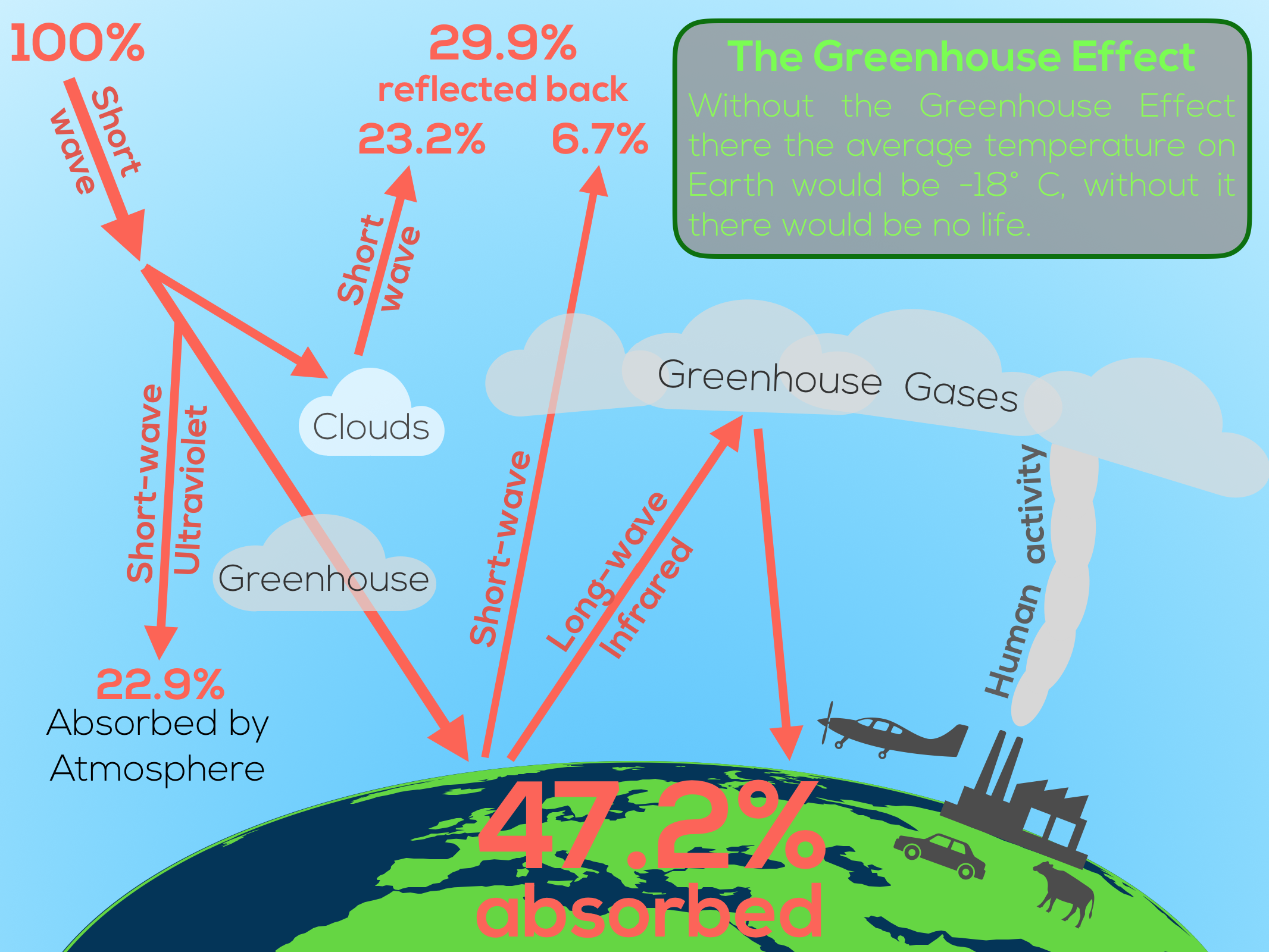



Global Climate Dp Geography Ib Recap




Greenhouse Effect National Geographic Society




Ib Geography Global Climate Key Terms Flashcards Quizlet




The Albedo Effect The Influence Of Feedback Mechanisms In Climate Change Youtube




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming




Global Warming और Greenhouse Effect Environmental Science Letstute In Hindi Youtube




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Causes Of Global Climate Change Ib Geography Revision



Climate Change



2




8 1 Earth S Heat Budget Introduction To Oceanography



2



The Energy Balance Geography Myp Gcse Dp




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



Greenhouse Effect Zoom Astronomy



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic



1 Causes Of Global Climate Change The Geographer Online



The Concept Of Greenhouse Effect Assignment Point




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Teaching Climate Change American Federation Of Teachers



A Hiatus Of The Greenhouse Effect Scientific Reports




Atmosphere National Geographic Society




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Apes Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Ozone Layer Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Geography Finn Valley College



The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geography Myp Gcse Dp




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Heat Transfer In The Atmosphere Physical Geography




The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society




Understanding Greenhouse Effect Warming Of Earth Through Everyday Examples Youtube
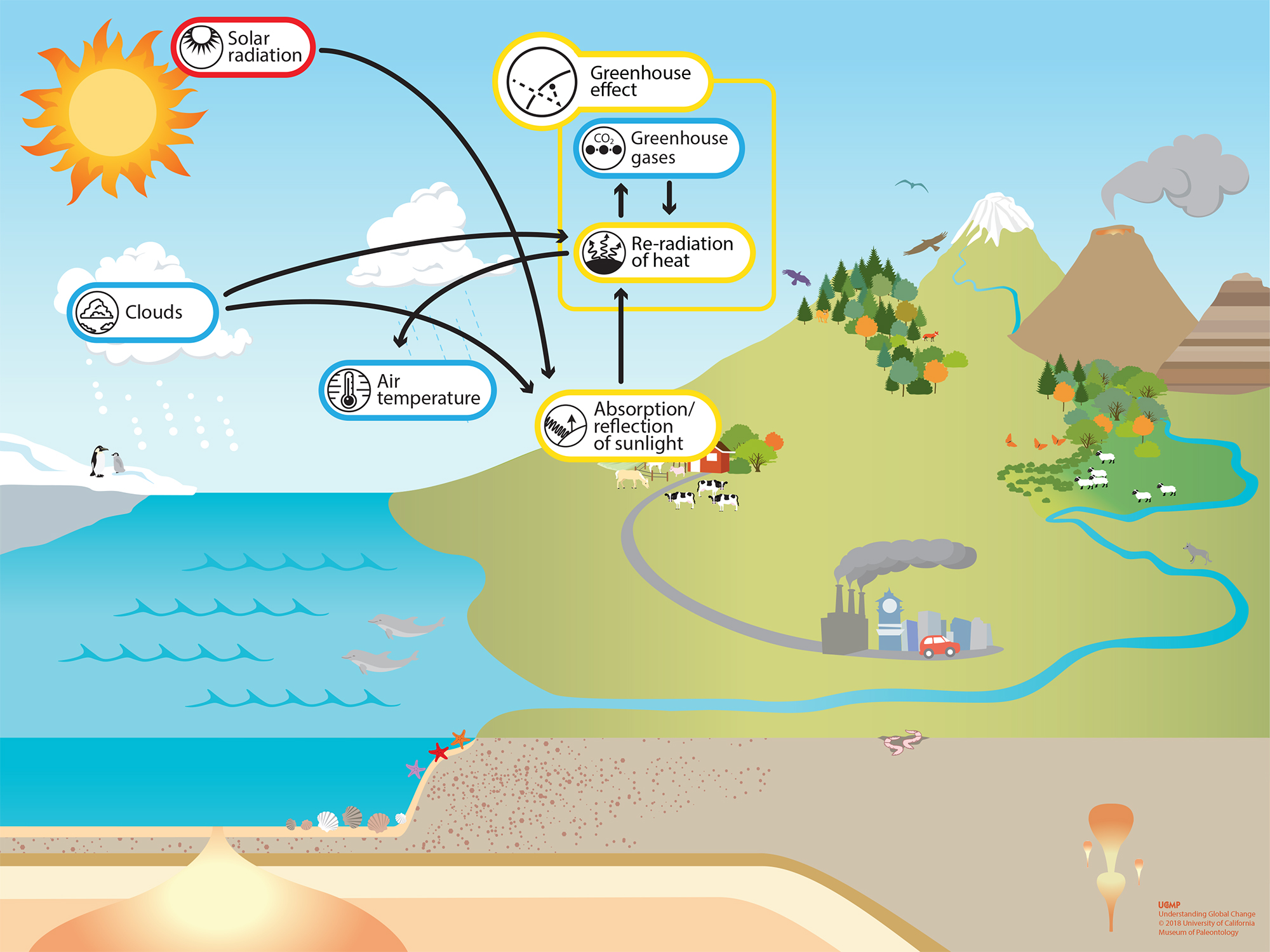



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change
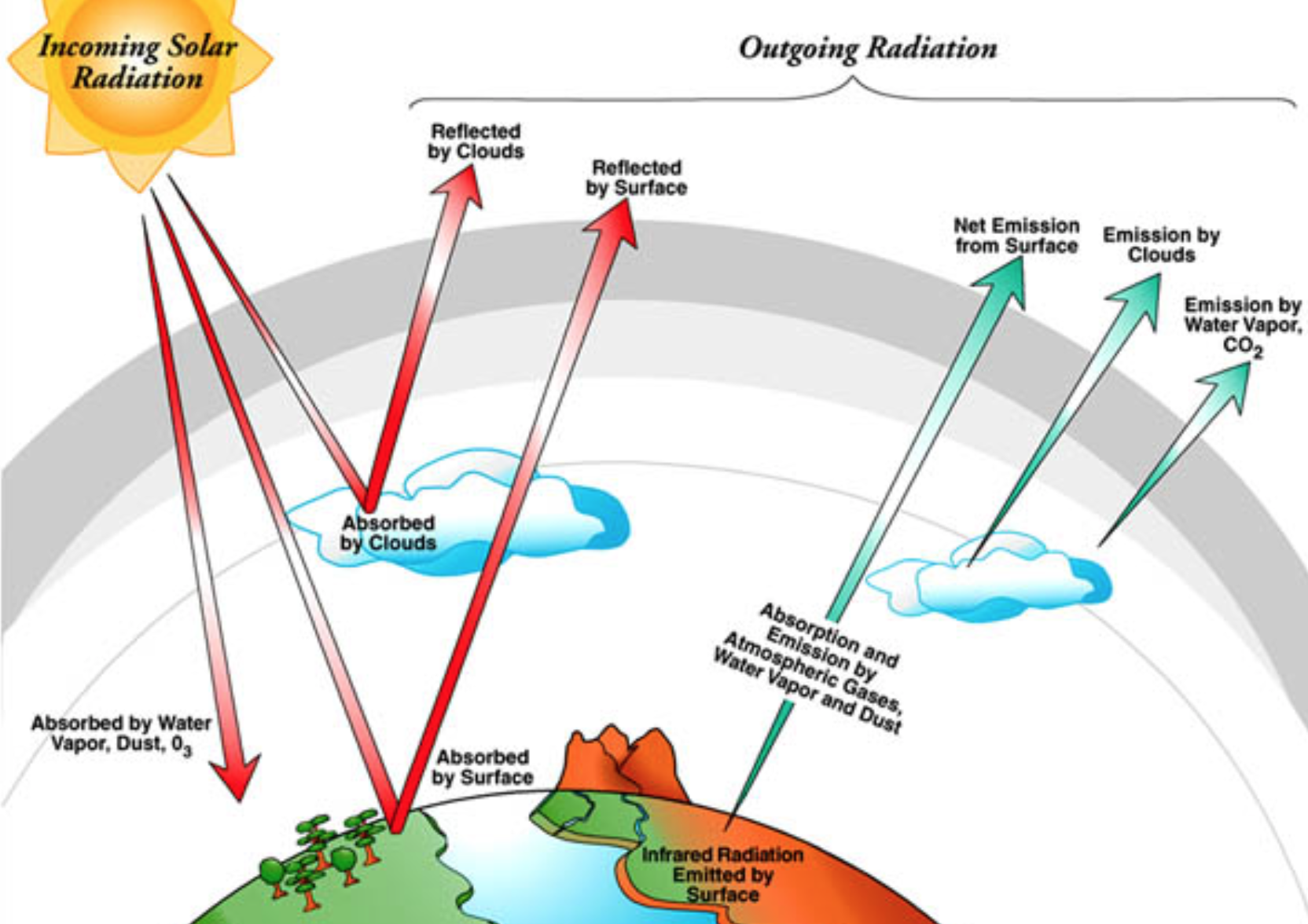



Atmospheric System Processes Buddinggeographers




The Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated
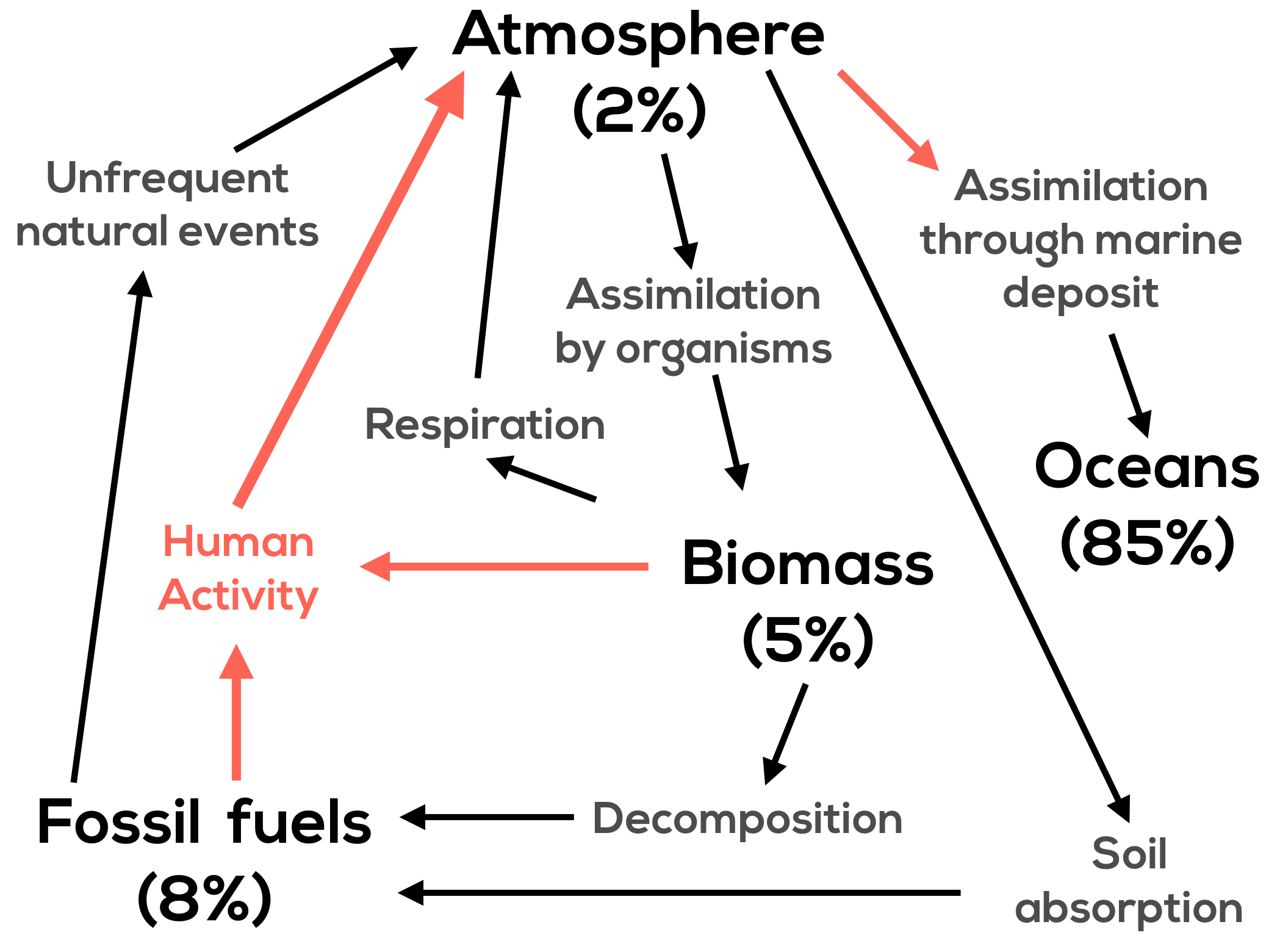



Global Climate Dp Geography Ib Recap



Ib Geography Environmental Sustainability




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




Higher Geography Global Warming Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect National Geographic Society




Implications Of Possible Interpretations Of Greenhouse Gas Balance In The Paris Agreement Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences




Climate Change Geography




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Video Khan Academy




Greenhouse Effect National Geographic Society



The Global Energy System



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias




Physics Of How Greenhouse Gases Trap Heat Pbs Learningmedia




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



7 H The Greenhouse Effect



Environment For Kids Global Warming




Geography Global Warming Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Vector Illustration Educational Poster Scientific Infographic And Presen Greenhouse Effect Education Poster Presentation Templates



The Global Energy System




Chapter 3 Physical Geography Climate And Vegetation Climate



Greenhouse Effect



3
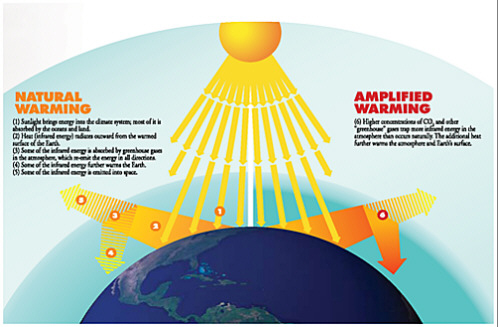



2 What We Know About Climate Change And Its Interactions With People And Ecosystems Advancing The Science Of Climate Change The National Academies Press
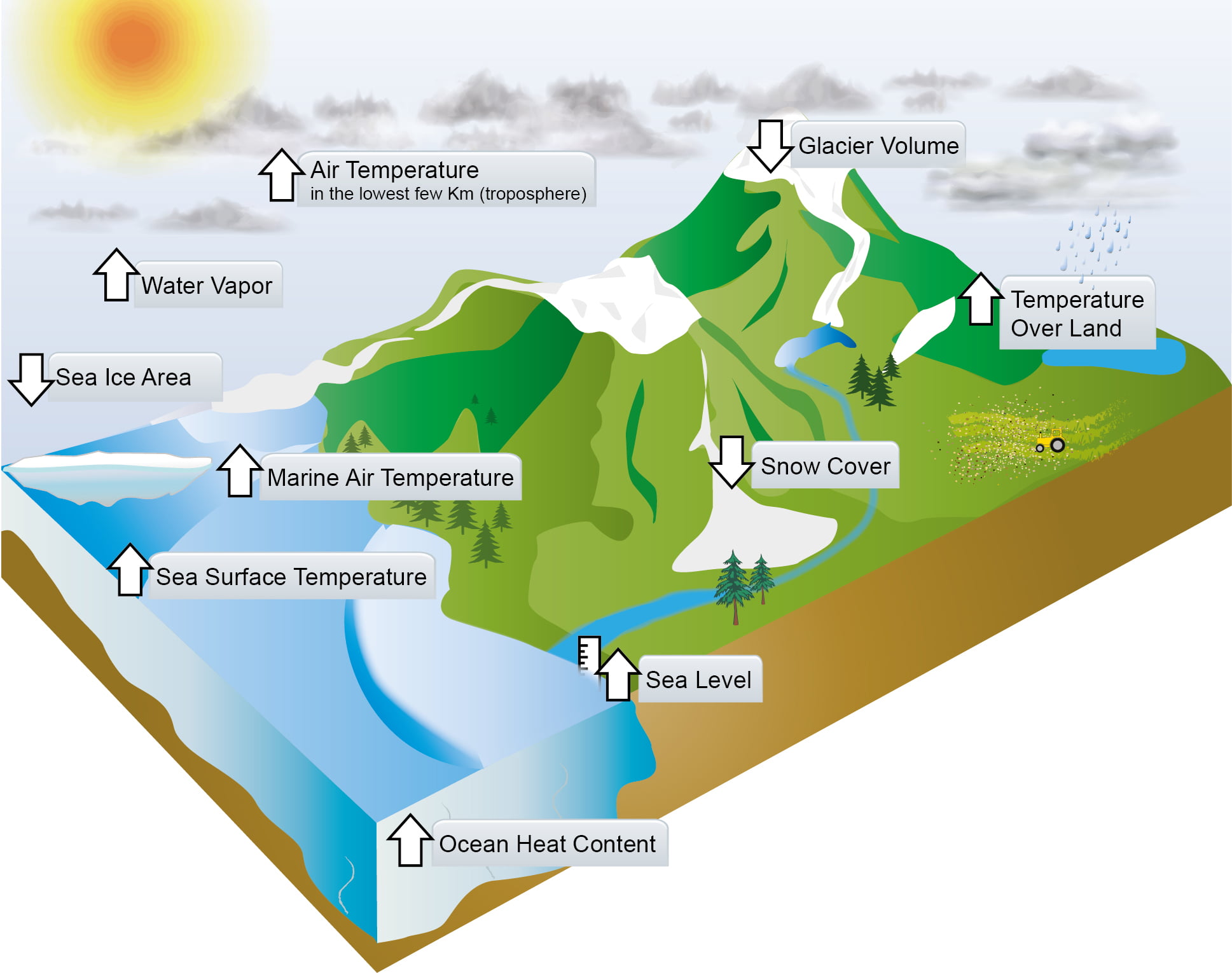



Metlink Royal Meteorological Society Ipcc Updates For Geography Teachers




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay



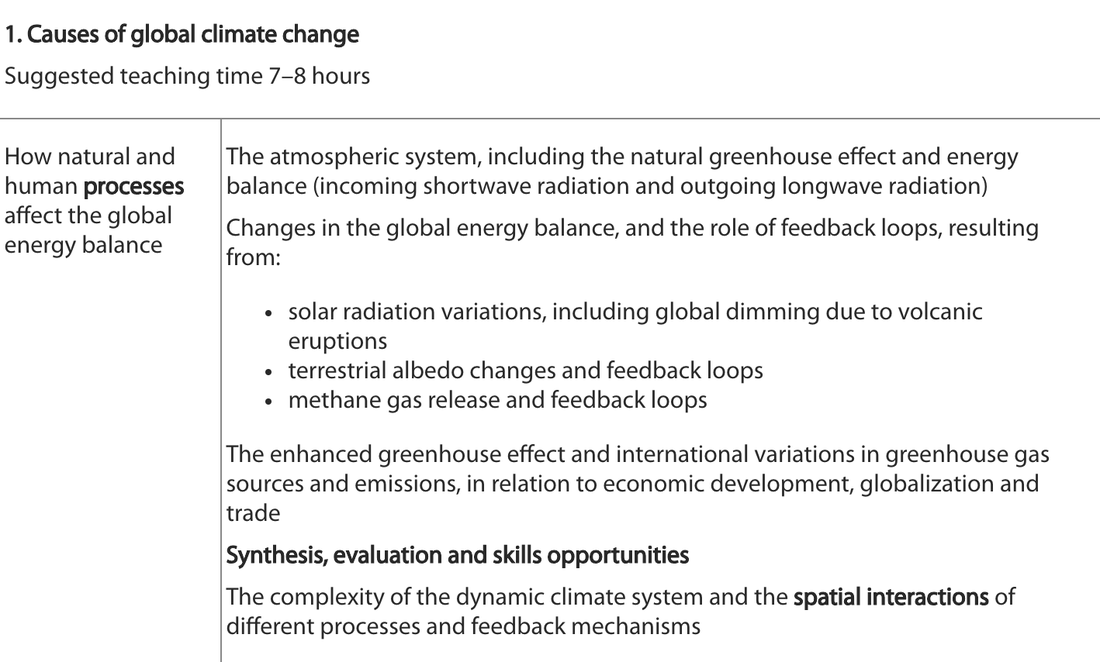
2 2 1 Causes Of Global Climate Change




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect



Why Is The Greenhouse Effect Called So In Geography Quora




Greenhouse Effect On Earth Assignment Point




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Global Warming Ks2 Geography




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Nanostructured Metal Oxide Semiconductor Based Sensors For Greenhouse Gas Detection Progress And Challenges Royal Society Open Science



2 2 1 Causes Of Global Climate Change




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram




Gcse Unit 1 Challenges For The Planet Geography Is Easy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿